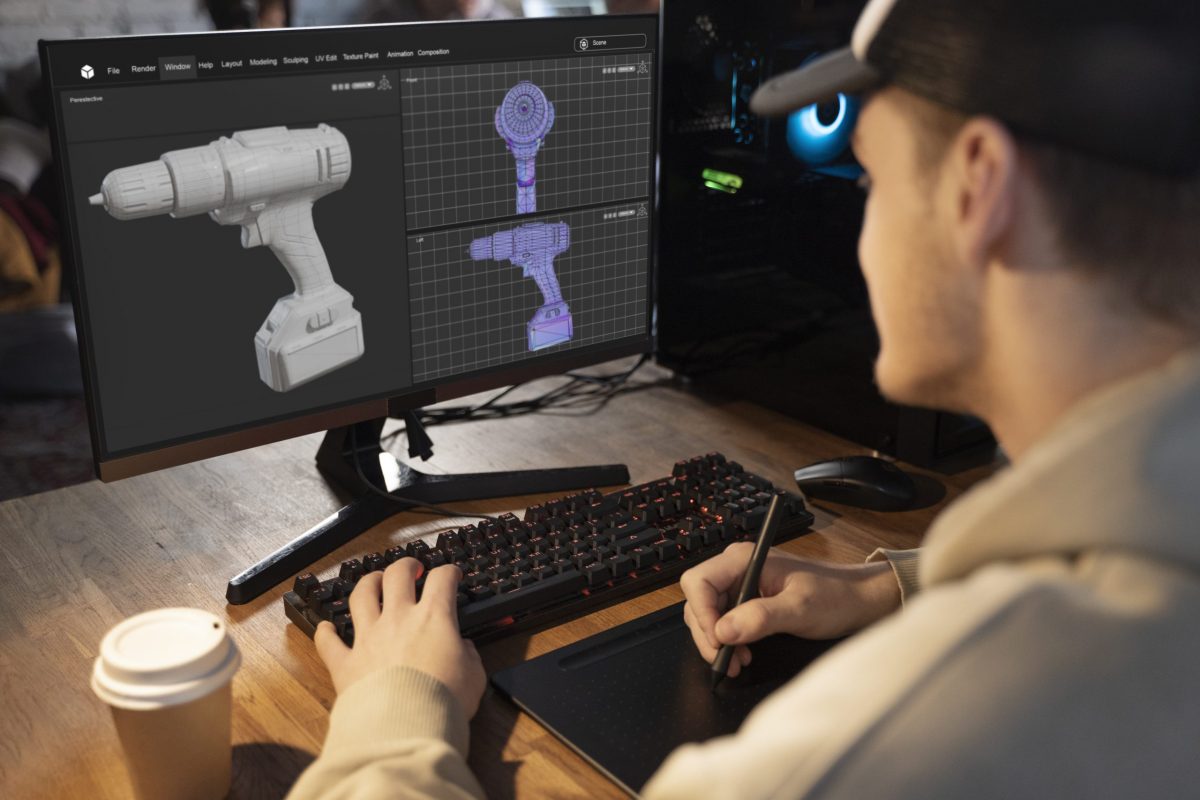

In the world of animation, 3D modeling plays a vital role in bringing characters and environments to life. Whether you are a beginner looking to start a career in animation or an experienced artist seeking to refine your skills, mastering 3D modeling is essential to creating captivating and realistic animations. In this article, we will explore the key aspects of 3D modeling for animation and provide you with valuable insights to help you embark on a successful journey in the world of 3D animation.
Table of Contents
- Introduction
- Understanding the Basics of 3D Modeling
- What is 3D modeling?
- Types of 3D modeling software
- Essential tools and features
- Mastering 3D Modeling Techniques
- Creating organic shapes and characters
- Designing props and objects
- Constructing realistic environments
- Texturing and UV Mapping
- Applying textures to 3D models
- Unwrapping UV maps for realistic rendering
- Utilizing materials and shaders
- Rigging and Animation
- Setting up skeletal systems for characters
- Animating 3D models
- Understanding keyframes and timelines
- Lighting and Rendering
- Setting up lights for different moods
- Exploring rendering settings
- Optimizing render times
- Advanced 3D Modeling Techniques
- Character facial rigging
- Cloth simulation
- Particle systems and special effects
- Industry Trends and Software
- Staying up-to-date with the latest advancements
- Popular 3D modeling software in the industry
- Tips for Improving 3D Modeling Skills
- Practice regularly
- Learn from tutorials and resources
- Seek feedback and constructive criticism
- Building a Strong Portfolio
- Showcasing your best works
- Tailoring your portfolio for job applications
- Career Opportunities in 3D Animation
- Animation studios
- Gaming industry
- Film and television production
- Overcoming Common Challenges
- Dealing with creative blocks
- Managing project timelines
- Balancing creativity and technicality
- Conclusion
- FAQs
Introduction
The art of 3D modeling for animation is a fascinating and versatile skill that allows artists to create visually stunning worlds and characters that captivate audiences of all ages. From animated movies and television shows to video games and virtual reality experiences, 3D modeling is at the heart of modern storytelling and entertainment. Whether you want to create whimsical creatures or realistic architectural designs, mastering 3D modeling opens up a world of creative possibilities.
Understanding the Basics of 3D Modeling
What is 3D Modeling?
At its core, 3D modeling is the process of creating digital representations of objects and characters using specialized software. Instead of traditional flat images, 3D models are built in three dimensions, allowing artists to add depth, texture, and realism to their creations. It involves shaping and manipulating virtual polygons to construct the desired form, whether it’s a simple cube or a complex character.
Types of 3D Modeling Software
There is a wide range of 3D modeling software available in the market, each catering to different skill levels and specific requirements. Some popular options include Blender, Autodesk Maya, Cinema 4D, and ZBrush. Beginners can start with user-friendly software, while advanced artists may prefer more feature-rich tools.
Essential Tools and Features
To become proficient in 3D modeling, it’s crucial to familiarize yourself with the essential tools and features offered by the software. These may include basic shape creation, sculpting brushes, mesh editing tools, modifiers, and more. Understanding how to use these tools effectively is fundamental to producing high-quality 3D models.
Mastering 3D Modeling Techniques
Creating Organic Shapes and Characters
Designing organic shapes, such as human characters or animals, requires a keen eye for proportions and anatomy. Learning to sculpt intricate details and using reference images can significantly enhance the realism of your creations.
Designing Props and Objects
In addition to characters, animators often need to model props and objects that populate their 3D worlds. This could range from simple everyday items to complex machinery or fantastical artifacts.
Constructing Realistic Environments
Building immersive environments that serve as backdrops for your animations is a crucial skill. Understanding architecture, lighting, and composition helps in creating believable and visually appealing settings.
Texturing and UV Mapping
Applying Textures to 3D Models
Textures add visual richness and detail to 3D models. Mastering texture application involves understanding different mapping techniques and how to paint or import textures onto your models.
Unwrapping UV Maps for Realistic Rendering
UV mapping is the process of “unwrapping” a 3D model to create a 2D representation, which allows textures to be applied accurately. Proper UV mapping is essential for achieving realistic rendering results.
Utilizing Materials and Shaders
Materials and shaders control how light interacts with the surfaces of your 3D models. Learning to use various material properties and shaders enhances the realism and visual appeal of your animations.
Rigging and Animation
Setting up Skeletal Systems for Characters
Rigging involves creating a skeletal structure for characters, allowing them to move and pose realistically. Understanding joint placement and weight painting is crucial for smooth and lifelike animations.
Animating 3D Models
Animation breathes life into static 3D models. Learning the principles of animation, such as timing, anticipation, and follow-through, is essential for creating compelling character movements.
Understanding Keyframes and Timelines
Keyframes are specific points in an animation where important poses or changes occur. Organizing keyframes on a timeline allows you to control the movement and progression of your animations.
Lighting and Rendering
Setting up Lights for Different Moods
Lighting sets the tone and mood of your animations. Mastering lighting techniques, such as three-point lighting or global illumination, adds depth and atmosphere to your scenes.
Exploring Rendering Settings
Rendering is the process of converting your 3D scene into a final image or video. Understanding rendering settings and output options is essential for producing high-quality animated sequences.
Optimizing Render Times
Rendering can be a time-consuming process. Learning optimization techniques, such as using render layers and proxies, can significantly reduce render times without compromising quality.
Advanced 3D Modeling Techniques
Character Facial Rigging
Facial expressions are crucial for conveying emotions in character animations. Advanced facial rigging techniques enable animators to achieve realistic and expressive facial movements.
Cloth Simulation
Simulating cloth movement and behavior adds a layer of realism to characters and environments. Understanding cloth simulation tools and parameters is valuable for achieving believable fabric motion.
Particle Systems and Special Effects
Particle systems allow artists to create effects like smoke, fire, water, and explosions. Mastering particle systems empowers animators to craft stunning visual effects in their animations.
Industry Trends and Software
Staying Up-to-Date with the Latest Advancements
The field of 3D modeling and animation is continually evolving. Staying informed about industry trends, new software updates, and emerging techniques is vital for remaining competitive.
Popular 3D Modeling Software in the Industry
Different industries may favor specific 3D modeling software. Understanding the software used in your chosen field helps you tailor your skills to meet industry demands.
Tips for Improving 3D Modeling Skills
Practice Regularly
Like any skill, practice is essential for improvement. Regularly engaging in 3D modeling projects and exercises hones your abilities and builds your portfolio.
Learn from Tutorials and Resources
The internet is filled with tutorials, forums, and resources on 3D modeling. Learning from experienced artists and peers can provide valuable insights and shortcuts.
Seek Feedback and Constructive Criticism
Feedback from fellow artists or mentors helps identify areas for improvement. Being open to constructive criticism fosters growth as a 3D artist.
Building a Strong Portfolio
Showcasing Your Best Works
A well-curated portfolio showcases your best 3D modeling projects. Highlighting your skills and versatility can attract potential employers or clients.
Tailoring Your Portfolio for Job Applications
Customizing your portfolio to align with the job you’re applying for can make you stand out among other candidates. Tailor your selection to demonstrate skills relevant to the position.
Career Opportunities in 3D Animation
Animation Studios
Animation studios work on projects like movies, television shows, and commercials. Joining a studio offers opportunities to work on large-scale productions.
Gaming Industry
The gaming industry demands 3D modelers to create characters, environments, and assets for video games. Game development studios are always in search of skilled 3D artists.
Top 5 Programming Languages You Should Learn for Game Development
Unity 3D Developer Jobs: A Growing Field in the World of Game Development
Film and Television Production
Film and TV production often require 3D modeling for special effects, set design, and visual elements. Joining the film and television industry allows you to contribute to diverse projects.
Overcoming Common Challenges
Dealing with Creative Blocks
Creative blocks are common in any artistic pursuit. Exploring different sources of inspiration and taking breaks can help overcome these hurdles.
Managing Project Timelines
Effective time management is crucial for meeting deadlines and ensuring the quality of your work. Breaking down projects into manageable tasks helps stay on track.
Balancing Creativity and Technicality
Being a 3D modeler involves both artistic creativity and technical know-how. Balancing these aspects ensures that your models are both visually appealing and structurally sound.
Low Poly 3D Models: Exploring the Art of Simplified Polygonal Designs
Learn 3D Modeling in 2023: A Comprehensive Guide
Conclusion
Mastering 3D modeling for animation is a rewarding journey that unlocks boundless creative opportunities. By understanding the fundamentals, honing essential techniques, and staying updated on industry trends, you can become a proficient 3D modeler capable of bringing imaginative worlds to life.
FAQs
- Q: How long does it take to learn 3D modeling for animation? A: The time it takes to become proficient in 3D modeling varies depending on individual dedication and practice. It may take several months to a few years to achieve mastery.
- Q: Can I learn 3D modeling on my own, or do I need formal education? A: While formal education can provide a structured learning environment, many artists learn 3D modeling through online tutorials and self-guided practice.
- Q: Which software is best for beginners in 3D modeling? A: Blender is an excellent choice for beginners as it is free, user-friendly, and offers a wide range of tools and features.
- Q: Are 3D modelers in high demand in the job market? A: Yes, 3D modelers are in demand in various industries, including animation, gaming, and architecture.
- Q: How important is a strong portfolio for landing 3D modeling jobs? A: A strong portfolio is crucial as it showcases your skills and demonstrates your suitability for potential job opportunities.

















Leave a Comment